Hibernate - Inheritance – Strategy 2 : Table Per Sub Class Hierarchy
Inheritance – Strategy 2 : Table Per Sub Class Hierarchy
Inheritance
Mapping
Hibernate
supports 3 basic inheritance mapping strategies.
1.
Table per class hierarchy
2.
Table per subclass
3.
Table per concrete class
By
using Primary key / Foreign key concept subclass are mapped with its
parent class.
As
per the below example there will be 3 tables and no relations to
each other.
To
do the table map, use joined-subclass
element.
<joined-subclass
name="pojo.PermanentEmployee"
table="permanentemployee">
<key
column="eid"></key>
<property
name="salary"></property>
<property
name="bonus"></property>
</joined-subclass>
The
Key subelement
of joined-subclass is used to generate the foreign
key.
Since
we are using hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto
property it generates the
tables automatically. So no need to worry about creating tables in
the database.
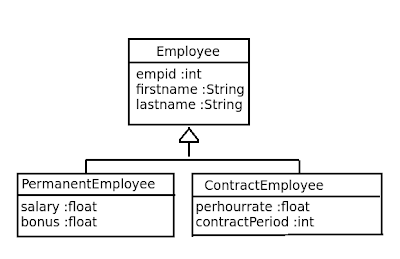
Suppose
you have the base Employee class, with PermanentEmployee
and ContractEmployee as subclasses.
Steps -
Step
1 - Create POJO classes ( Employee.java and PermanentEmployee,
ContractEmployee sub-classes )
Step
2 - Create mapping file ( employee.hbm.xml )
Step
3 - Hibernate Configurations ( hibernate.cfg.xml )
Step
4
- Create class to do the execution ( ExecuteEmployee.java )
Step
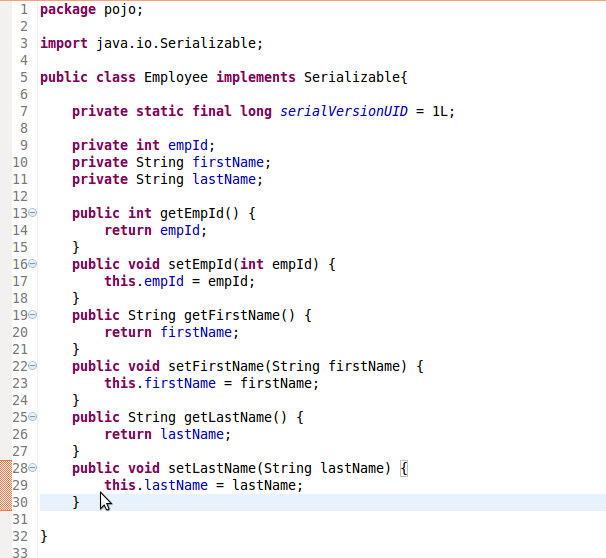
1 - Create POJO classes
Create
POJO (Plain Old Java Object) classes that represents the Employee,
PermanentEmployee and ContractEmployee.


Step
2 - Create mapping file
Create
a mapping file “employee.hbm.xml” which maps, “employee”,
“permanentemployee”, “contractemployee” tables in the
database by using <union-subclass
tag.
<joined-subclass
name="pojo.PermanentEmployee"
table="permanentemployee">
<key
column="eid"></key>
..
</joined-subclass>

Step
3 - Hibernate Configurations
Create
configuration file name as hibernate.cfg.xml and save it.

Step
4 - Create Execute class
Create
a ExecuteEmployee class to do the execution.




Out
put on the above application as follows.
