Hibernate ( Annotation ) - 1st Program
First Hibernate ( Annotation ) Application
The
Hibernate application can be created with annotation. There are many
annotations which can be created Hibernate application such as
@Entity, @Id, @Table etc.
Hibernate
Annotations are based on JPA 2 specification and it supports all the
features.
JPA
annotations are defined in javax.persistance.*
package
Hibernate
EntityManager implements
the Interfaces and life cycle defined by the JPA specificatoin.
Hibernate
annotations are used to provide the meta data.
Core
Advantage use of Annotations – no need to create mapping files (
.hbm.xml )
For this example we use below annotations
@Entity annotation – marks the class as entity.
@Table annotation – specifies the table name where data of this entity is to be persisted. ( note – if not specify the @Table annotation, by default hibernate use as the class name for that )
For this example we use below annotations
@Entity annotation – marks the class as entity.
@Table annotation – specifies the table name where data of this entity is to be persisted. ( note – if not specify the @Table annotation, by default hibernate use as the class name for that )
@Id
annotation – marks the identifier of this entity
@Column annotation – specifies the details of the column for this property or filed. ( note - if this not specify, property name will be used as the column name by default.) This lesson shows the basic steps of creating a simple hibernate application with hibernate annotation by using eclipse IDE.
@Column annotation – specifies the details of the column for this property or filed. ( note - if this not specify, property name will be used as the column name by default.) This lesson shows the basic steps of creating a simple hibernate application with hibernate annotation by using eclipse IDE.
Step
1 - Setup the development environment for Hibernate
Annotation
Step
2 - Create POJO class
( Employee.java )
Step
3 - Hibernate Configurations
plus add mapping to the configuration
( hibernate.cfg.xml )
Step
4
- Create class to do the execution ( ExecuteEmployeeAnnotation.java )
Step
1 - Setup the development environment for Hibernate
To
set up the development environment you need to carry out below
operations.
(
Assume
* you
already install Java to your development environment
* you
already add the hibernate related libraries to the project through
eclipse IDE.
* Create
a table in the MySQL database – for this example I create the
table called “employeeannotation”
and empid is the primary key)
Step
1.1 Add Hibernate Annotation Prerequisites
For
use annotation, it uses
* ejb3-persistence.jar
* hibernate-annotations.jar
* hibernate-commons-annotations.jar
Create
a new lib folder under your project and copy above files into the lib
folder. Once you copy the files, then
you need to configure the build path. For that use below steps.
i)
Right click the project
ii)
Select Build Path
iii)
Configure Build Path
iv)
Go to Libraries tab and browse and add all jar files
Step
2 - Create POJO class
Create
a POJO (Plain Old Java Object) class that represents the employee.
This is a simple class which has property getter and setter methods
and private visibility for the fields. Additionally we create the
annotation here.
Step
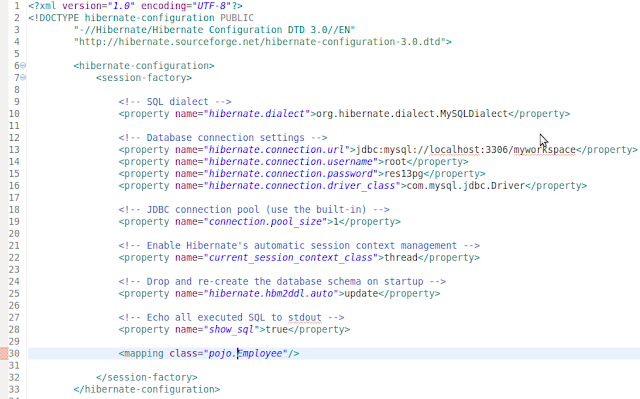
3 - Hibernate Configurations plus add mapping to the configuration
Step
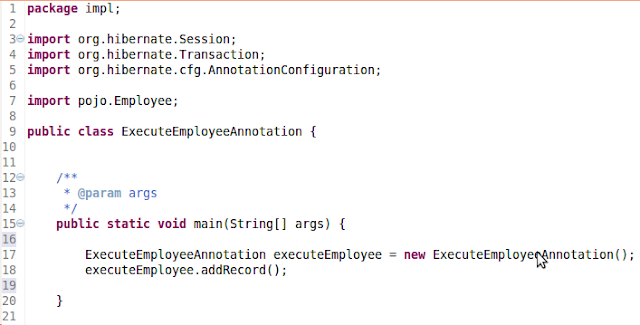
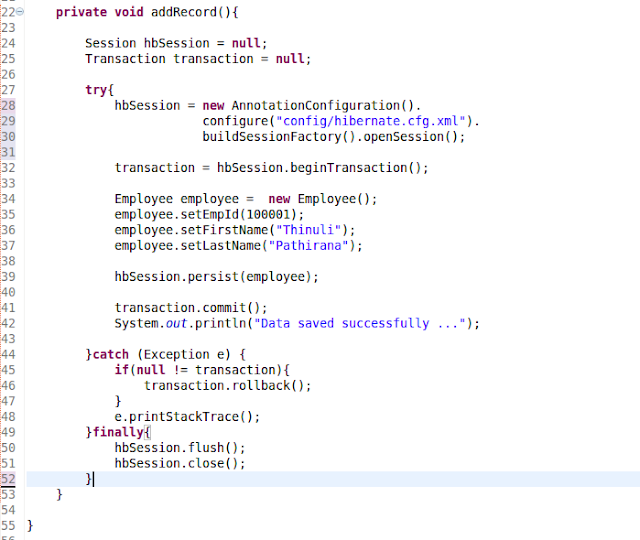
4 - Create class to do the
execution
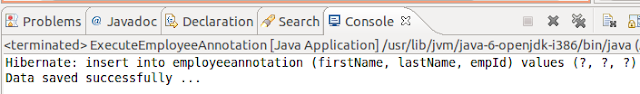
Out
put on the above application as follows.