HIbernate - Inheritance – Strategy 3 ( with Annotation ) : Table Per Concrete Class Hierarchy
Third Hibernate Annotation Application ( Inheritance – Strategy 3 : Table Per Class Hierarchy )
Inheritance
Mapping
Hibernate
supports 3 basic inheritance mapping strategies.
1.
Table per class hierarchy
2. Table per subclass
2. Table per subclass
3. Table
per concrete class
As
per the below example there will be 3 tables and no relations to
each other.
There
is no null values in the table since tables are created per class.
Disadvantage
of this approach is, it created duplicate columns.
For
this example we use below assotations.
@Inheritance(
strategy = InheritanceType.TABLE_PER_CLASS)
- specifies we use Table per class strategy.
@AttributeOverrides({
@AttributeOverride(
name = "empId",
column = @Column(name
= "empId")),@AttributeOverride( name = "firstName", column = @Column(name = "firstName")),
@AttributeOverride( name = "lastName", column = @Column(name = "lastName"))
})
- Parent calls attributes got override in Child classes.
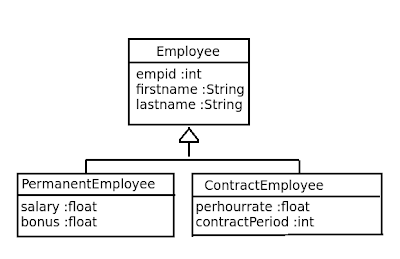
Suppose you have the base Employee class, with PermanentEmployee and ContractEmployee as subclasses.
Steps -
Step
1 - Create POJO classes ( Employee.java and PermanentEmployee,
ContractEmployee sub-classes )
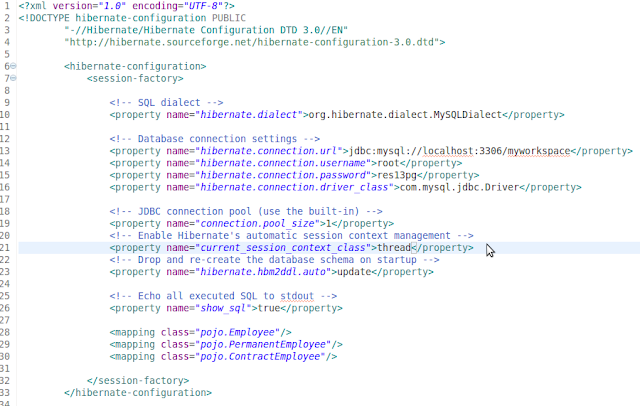
Step 2 - Hibernate Configurations ( hibernate.cfg.xml )
Step 3
- Create class to do the execution ( ExecuteEmployee.java )
Step 1 - Create POJO classes
Step 1 - Create POJO classes
Create
POJO (Plain Old Java Object) classes that represents the Employee,
PermanentEmployee and ContractEmployee.



Step 2 - Hibernate Configurations
Create configuration file name as hibernate.cfg.xml and save it.
Step 3 - Create Execute class
Create
a ExecuteEmployee class to do the execution.




Out put on the above application as follows.
